Experimental characterization and theoretical analysis of cell tip oscillations in directional solidification
Résumé
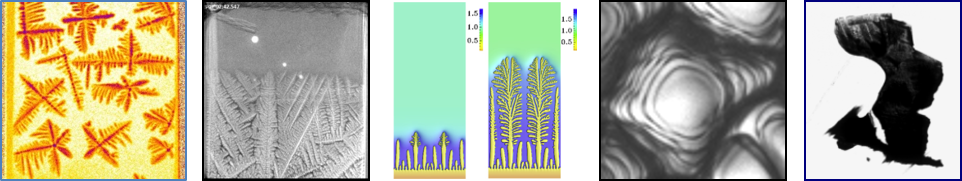
Experiments performed in DECLIC-DSI on board the International Space Station evidenced oscillatory modes during the directional solidification of a bulk sample of succinonitrile-based transparent alloy. The interferometric data acquired during a reference experiment, V p = 1 μm/s and G = 19 K/cm, allowed us to reconstruct the cell shape and thus measure the cell tip position, radius, and growth velocity evolution, in order to quantify the dynamics of the oscillating cells. This study completes our previous reports [Bergeon et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 226102 (2013); Tourret et al., Phys. Rev. E 92, 042401 (2015); Pereda et al., Phys. Rev. E 95, 012803 (2017)] with, to our knowledge, the first complete monitoring of the geometric cell tip characteristics variations in bulk samples. The evolution of the shape, velocity, and position of the tip of the oscillating cells is associated with an evolution of the concentration field, inaccessible experimentally but mediating the diffusive interactions between the cells. The experimental results are supported by 3D phase-field simulations which evidence the existence of transversal solute fluxes between neighboring cells that play a fundamental role in the oscillation dynamics. The dynamics of oscillation of an individual cell is analyzed using a theoretical model based on classical equations of solidification through the calculation of the phase relationships between oscillation of the different tip characteristics.
| Origine | Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s) |
|---|
Loading...